WEB3bie
KNOW ABOUT Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network. An asset can be tangible (a house, car, cash, land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding).
Simple Concept
You (a node) have a file of transactions on your computer (a ledger). Two government accountants (let's call them miners) have the same file on theirs (so it’s distributed). As you make a transaction, your computer sends an e-mail to each accountant to inform them. Each accountant rushes to be the first to check whether you can afford it (and be paid their salary Bitcoins). The first to check and validate hits “REPLY ALL”, attaching their logic for verifying the transaction (proof of work). If the other accountant agrees, everyone updates their file… This concept is enabled by Blockchain technology.Blockchain is a combination of three leading technologies:
1. Cryptographic keys
2. A peer-to-peer network containing a shared ledger
3. A means of computing, to store the transactions and records of the network
Cryptography keys consist of two keys – Private key and Public key . These keys help in performing successful transactions between two parties. Each individual has these two keys, which they use to produce a secure digital identity reference. This secured identity is the most important aspect of Blockchain technology. In the world of cryptocurrency, this identity is referred to as ‘digital signature’ and is used for authorizing and controlling transactions.
The digital signature is merged with the peer-to-peer network ; a large number of individuals who act as authorities use the digital signature in order to reach a consensus on transactions, among other issues. When they authorize a deal, it is certified by a mathematical verification, which results in a successful secured transaction between the two network-connected parties. So to sum it up, Blockchain users employ cryptography keys to perform different types of digital interactions over the peer-to-peer network.
Why is Blockchain Popular?
Highly Secure
It uses a digital signature feature to conduct fraud-free transactions making it impossible to corrupt or change the data of an individual by the other users without a specific digital signature.Decentralized System
Conventionally, you need the approval of regulatory authorities like a government or bank for transactions; however, with Blockchain, transactions are done with the mutual consensus of users resulting in smoother, safer, and faster transactions.Automation Capability
To speed transactions, a set of rules — called a smart contract — is stored on the blockchain and executed automatically. A smart contract can define conditions for corporate bond transfers, include terms for travel insurance to be paid and much more.Immutable records
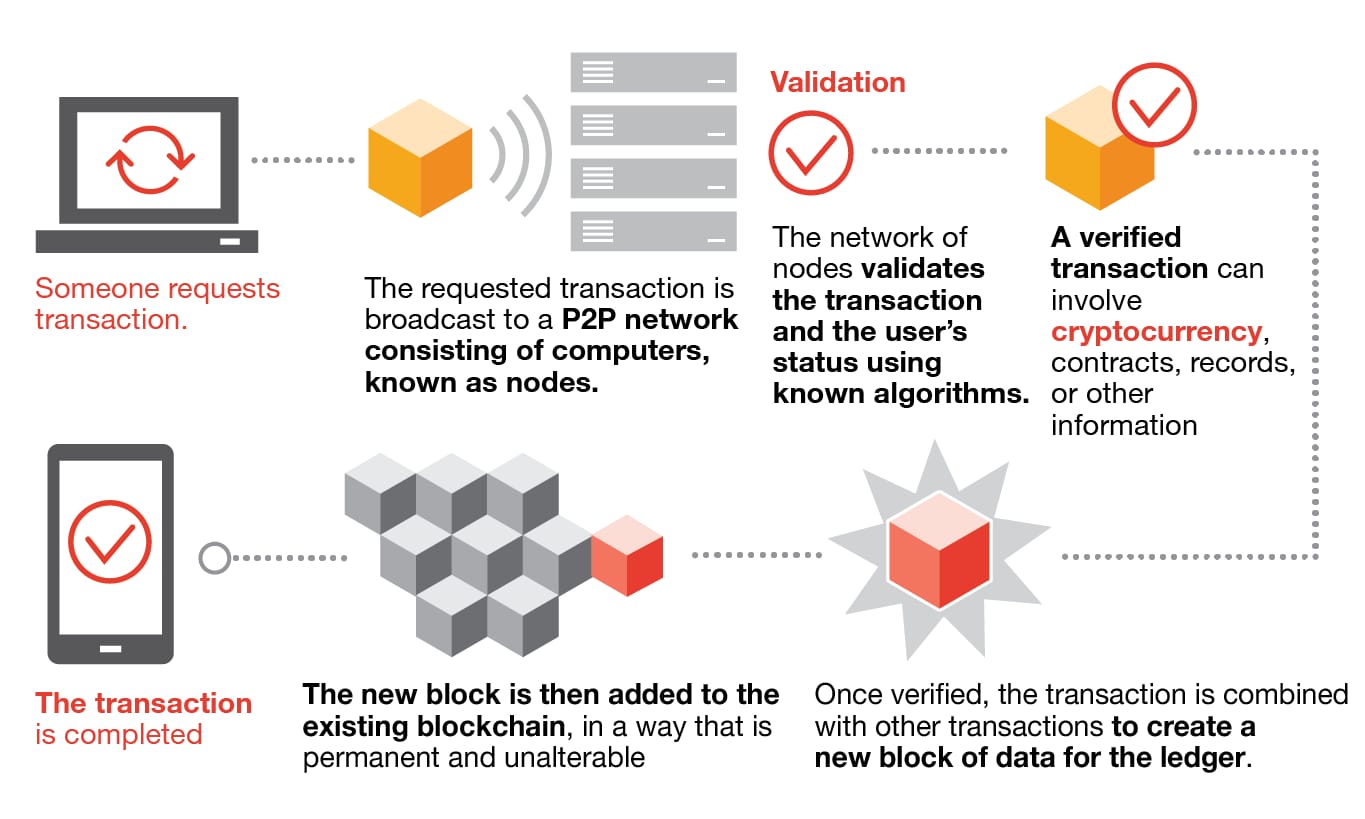
No participant can change or tamper with a transaction after it’s been recorded to the shared ledger. If a transaction record includes an error, a new transaction must be added to reverse the error, and both transactions are then visible.How blockchain works
As each transaction occurs, it is recorded as a “block” of data
Those transactions show the movement of an asset that can be tangible (a product) or intangible (intellectual). The data block can record the information of your choice: who, what, when, where, how much and even the condition — such as the temperature of a food shipment.Each block is connected to the ones before and after it
These blocks form a chain of data as an asset moves from place to place or ownership changes hands. The blocks confirm the exact time and sequence of transactions, and the blocks link securely together to prevent any block from being altered or a block being inserted between two existing blocks.Transactions are blocked together in an irreversible chain: a blockchain
Each additional block strengthens the verification of the previous block and hence the entire blockchain. This renders the blockchain tamper-evident, delivering the key strength of immutability. This removes the possibility of tampering by a malicious actor — and builds a ledger of transactions you and other network members can trust.Usage of blockchain
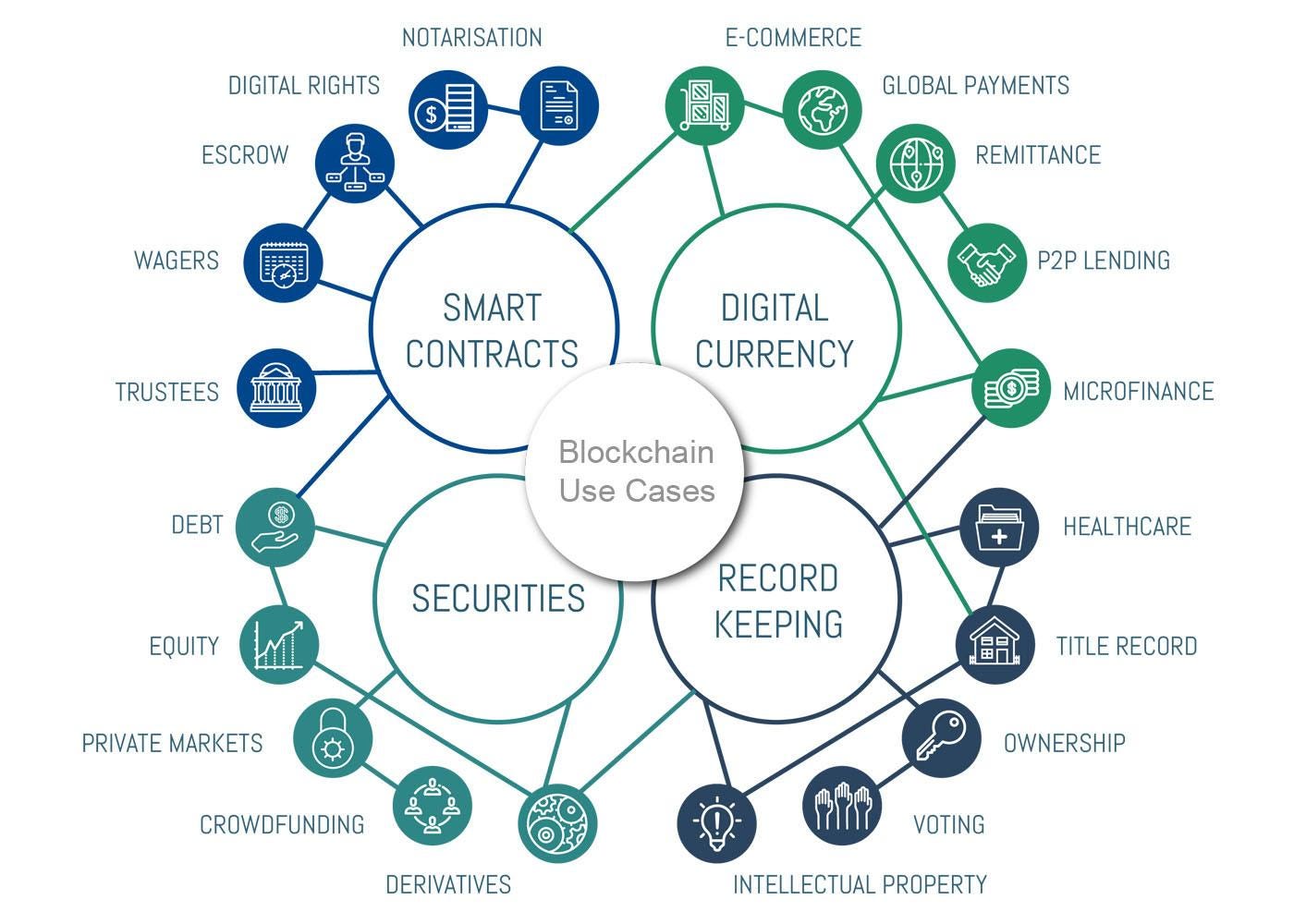
- Payment processing and money transfers
- Monitor supply chains
- Retail loyalty rewards programs
- Digital IDs
- Data sharing
- Copyright and royalty protection
- Digital voting
- Immutable data backup
- Tax regulation and compliance
- Equity trading
- Managing Internet of Things networks
WEB3bie

